 |
Disclaimer: The following article represents my personal viewpoint, an attempt to understand and explain the current state of the world. |
| Inspired by observing global trends, I propose a hypothesis to interpret ongoing events. I apply a straightforward approach: formulate the simplest hypothesis that could explain observed phenomena and retain it until disproven or until a simpler, more compelling explanation emerges. |
Introduction
The debate surrounding resource scarcity—most notably through the lens of “peak oil”—highlights the finite nature of critical resources such as oil, natural gas, and rare earth elements. French energy expert Jean-Marc Jancovici illustrates how resource extraction naturally peaks and then declines as reserves diminish.
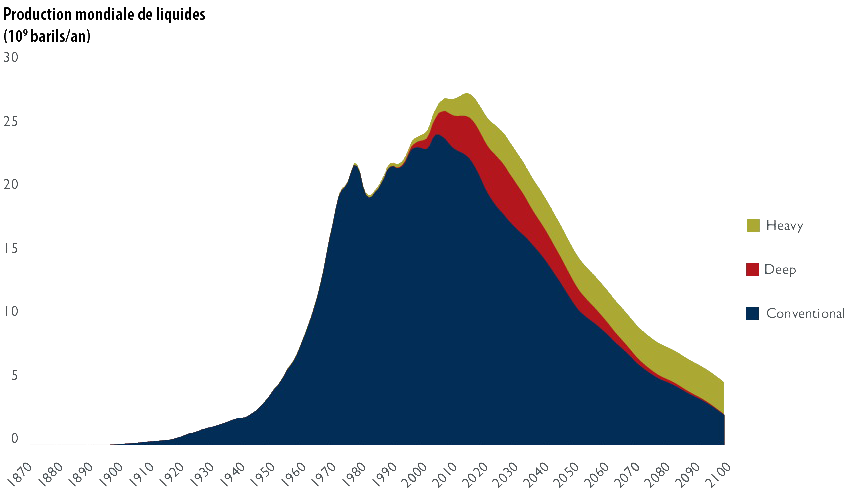
Explore Jancovici’s detailed perspective here.
Geologist Olivier Vidal extends this concept to rare earth metals, demonstrating the impact of declining ore quality and rising extraction costs—critical constraints for modern technologies:
The COVID Crisis: Preparing for Resource Constraints?
COVID-19 Lockdowns
During the COVID-19 pandemic, stringent lockdowns had pronounced economic consequences. A speculative interpretation is that such measures inadvertently prepared societies for reduced mobility and energy consumption—perhaps foreshadowing an era of limited resources. While intriguing, this theory remains speculative and open to debate.
Low-Emission Zones (ZFE)
In France, the establishment of Low-Emission Zones (ZFE) aims primarily at reducing air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. However, these zones also implicitly encourage reduced overall energy consumption by limiting vehicle use—a potentially intentional strategy amidst growing resource constraints.

Global Warming as Policy Justification
Although the reality of human-induced climate change is widely accepted, I question governments’ genuine commitment to combating climate change if economic competitiveness is at stake. Policies framed as climate measures might serve as a pretext for managing resource scarcity through controlled carbon emissions and energy usage.
The War in Ukraine: A Resource Conflict?
The ongoing conflict in Ukraine is multifaceted, with territorial sovereignty and geopolitical tensions dominating discussions. However, resource competition is increasingly cited as a significant factor. Ukraine’s substantial rare earth mineral deposits—reportedly over 50% of which lie in areas annexed or occupied by Russia—add complexity to the geopolitical stakes.
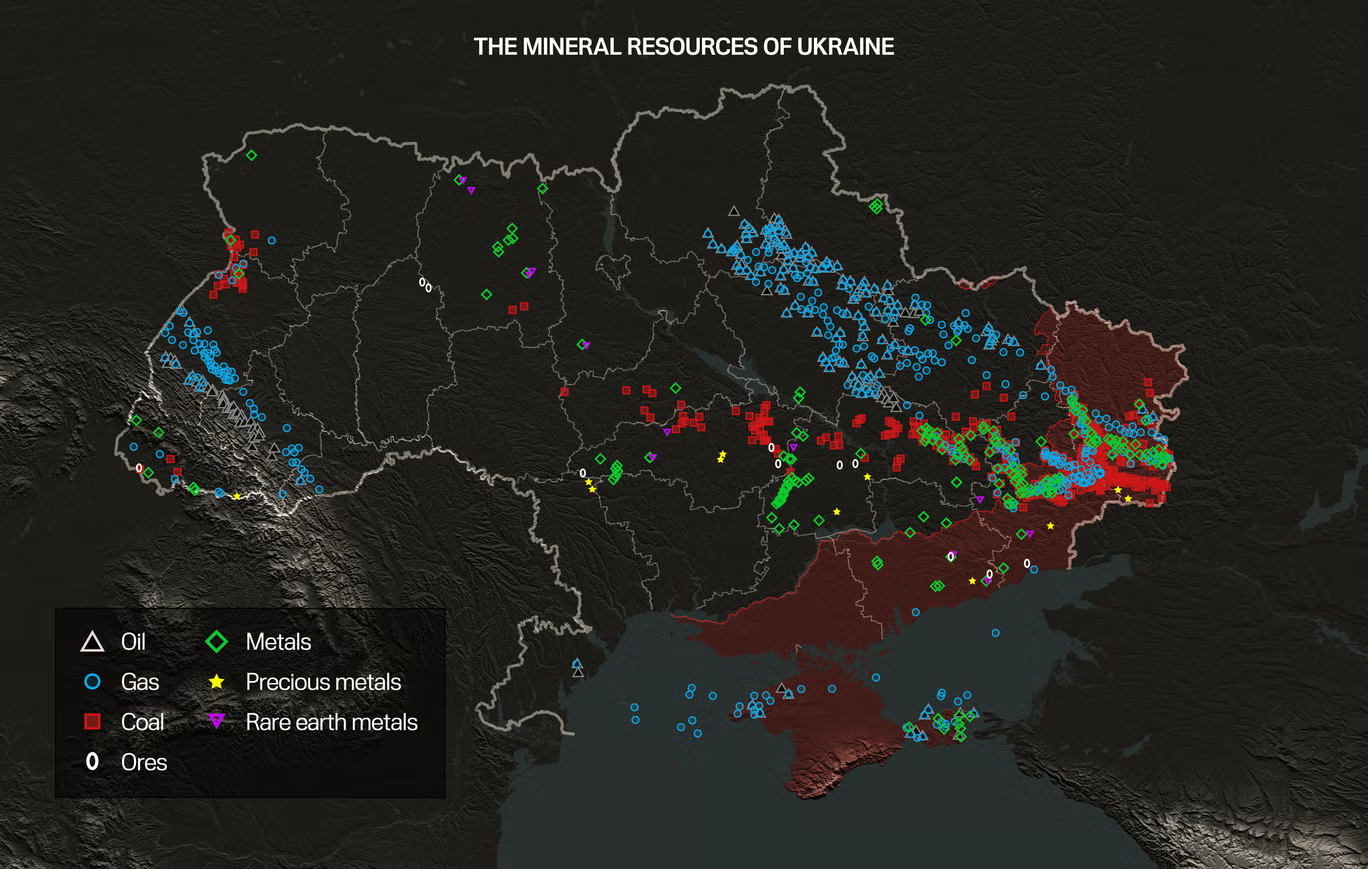
Detailed analysis can be found in The Independent’s recent coverage.
North American Ambitions: Trump’s Controversial Claims
Following his 2024 presidential victory, Donald Trump’s provocative statements regarding ambitions to annex Canada and Greenland—citing strategic resource interests—have sparked controversy and intense debate. Although the feasibility of such plans remains uncertain, the focus underscores growing geopolitical interest in resource-rich territories.
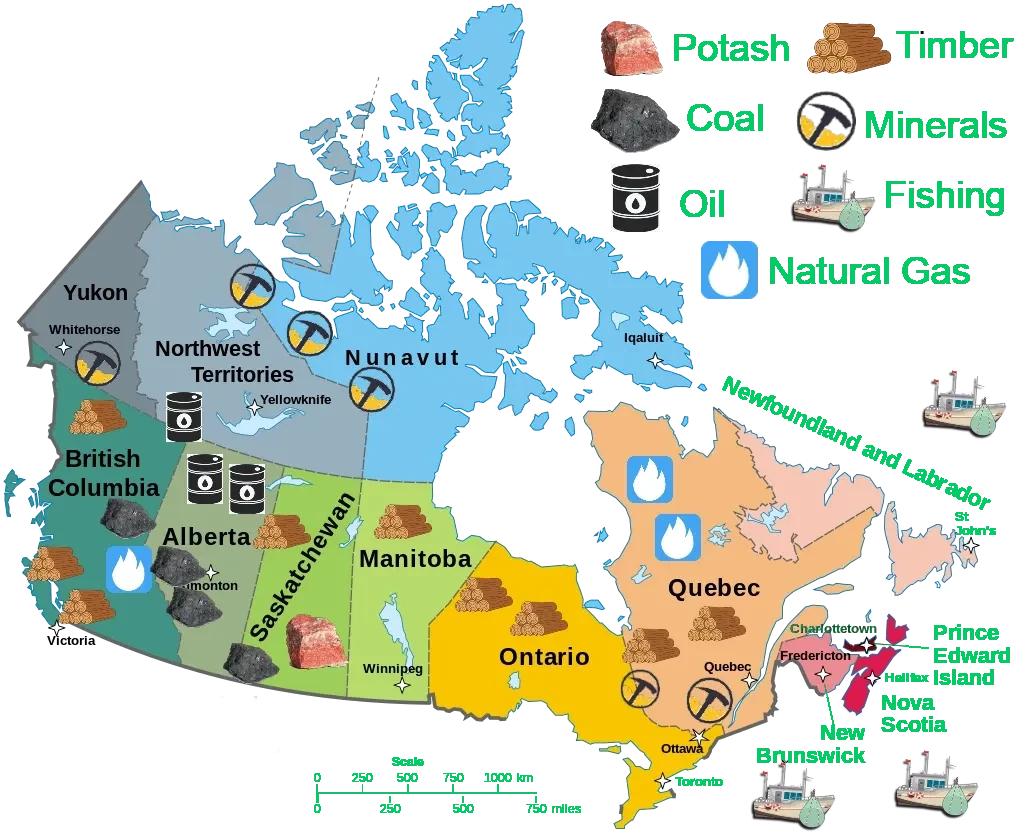
Coverage by CTV News highlights these controversial claims.
Energy Efficiency: The DPE System
France’s Diagnostic de Performance Énergétique (DPE) assesses building energy efficiency and greenhouse gas emissions. Poor ratings (F or G) impose rental restrictions, incentivizing energy efficiency upgrades and conservation efforts—illustrating another strategy to reduce resource consumption.
Comparable systems like the UK’s Energy Performance Certificates (EPCs) reflect similar objectives across Europe.
Further details available on the official DPE page.
The 15-Minute City: Resource-Efficient Urban Planning
The “15-minute city” concept promotes neighborhoods where residents have immediate access to essential services within walking or biking distance. Beyond environmental benefits, this urban planning model efficiently addresses resource scarcity by reducing dependency on energy-intensive transportation infrastructure.

Learn more from Wikipedia.
Digital Currencies: Balancing Innovation and Sustainability
The European Central Bank (ECB) explores the potential of a Digital Euro, raising concerns about its environmental impact. Blockchain-based currencies, particularly Proof-of-Work (PoW) systems, are energy-intensive, while alternatives such as Proof-of-Stake (PoS) or centralized ledger systems offer greater sustainability.
Annelieke A.M. Mooij (2022) argues that the ECB’s design choices must align with EU climate goals, potentially influencing the structure toward more energy-efficient models.
See the detailed analysis here.
Conclusion
Resource scarcity, environmental challenges, and geopolitical tensions are deeply interconnected. Policies targeting climate change, energy efficiency, or urban planning may simultaneously serve broader objectives: managing limited global resources amidst rising constraints.
 |
Disclaimer: These views are personal interpretations containing speculative elements. Readers should verify data through objective, peer-reviewed, and official sources. |